
https://www.timeanddate.com/calendar/march-equinox.html
There are two equinoxes every year – in March and September – when the Sun shines directly on the equator and the length of night and day are nearly equal.
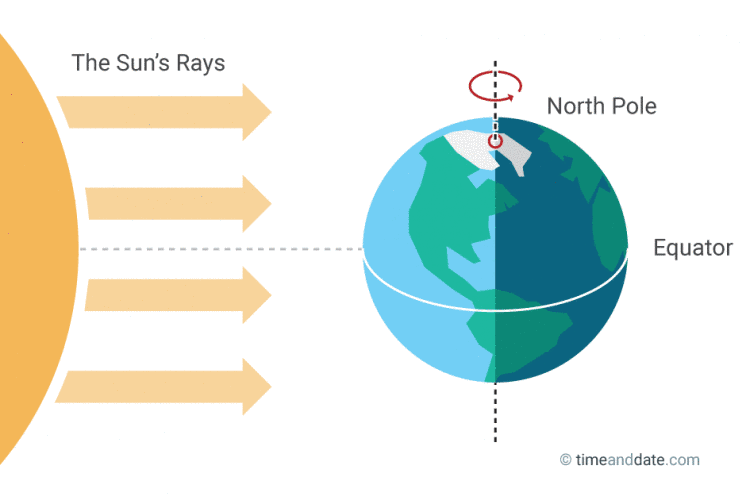
The March equinox marks the moment the Sun crosses the celestial equator – the imaginary line in the sky above the Earth’s equator – from south to north. This happens on March 19, 20, or 21 every year.
10 Facts About the March Equinox
https://www.abc.net.au/news/science/2017-09-01/seasons-and-their-changes-explained/8858776
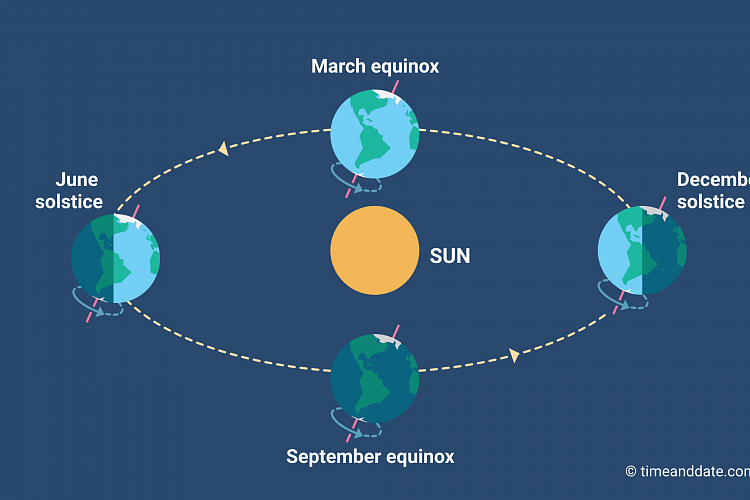
The seasons are a function of the Earth's tilt.
Some parts of the polar regions are so consistently cold — and the tropics so hot — they could pass for having only one season.
Even the sunniest Antarctic day is as cold as winter in most places. This is because the light reaching the bottom of the planet is at such a low angle it doesn't carry much heat.
On the other hand, the tropics are consistently hot. It doesn't matter if they're tilted towards or away from the Sun, they're still closer to it than anywhere else on Earth and they get plenty of direct light and heat.
But both places have two distinct seasons.

In the polar regions, the main difference comes down to the amount of daylight. During 'summer', the whole area is tilted towards the Sun and flooded with sunlight. Daytime at the poles lasts for half the year.
And the polar night lasts almost as long — making for one very long, dark winter.
In the tropics, the difference between seasons is due to rainfall.
The wet is caused by a permanent belt of storm clouds around the middle of the planet that dumps huge volumes of rain on the land or sea below. Thanks to the tilt of the planet and some super-sized sea breezes, the storm belt doesn't stay in one place. During the northern summer, the hot air over the land rises, sucking the storm belt as far north as the Tropic of Cancer, doling out monsoons wherever it goes.